Glass
Properties of glass
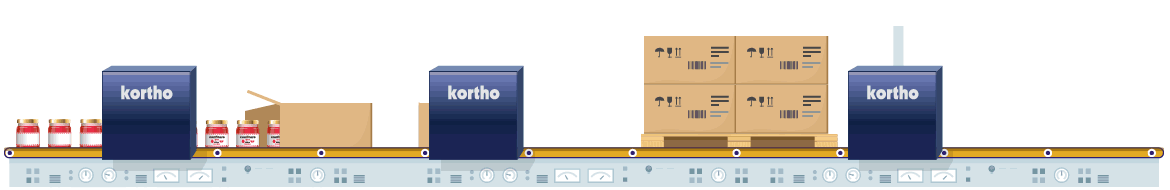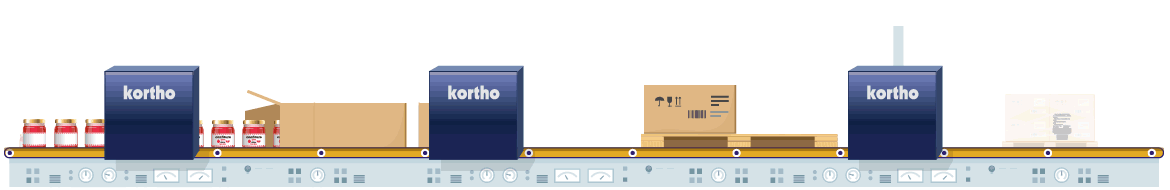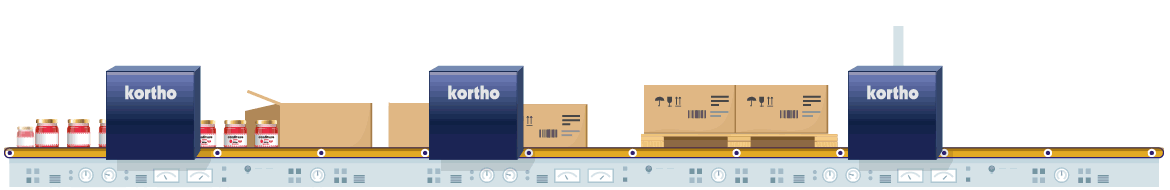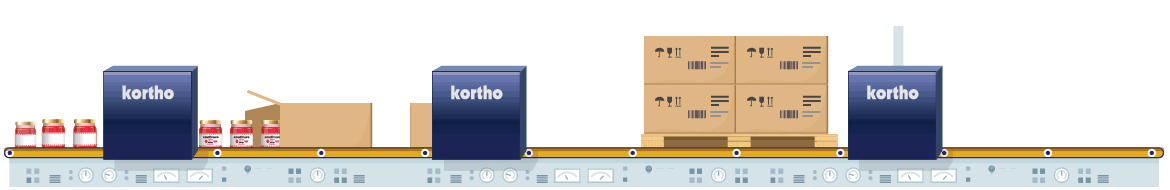
Glass is known as relatively difficult to code material. This is because glass has a very non-porous and densely structured surface. This means that it will not absorb liquids (such as oil based inks). This necessitates the use of UV-curable inks or solvent or wax-based inks. For solvent based inks, the solvent evaporates from the ink after coding, leaving the dye behind. Wax based inks adhere because they cool down and solidify on contact. As a final option there are UV-curable inks that dry after receiving a flash of UV light.
Suitable coding techniques for glass
Glass can be coded with Hi-Res Inkjet in combination with solvent based ink. Particularly in the food industry, individual product packaging is done while printing small codings such as best-before dates. The rapid evaporation of solvent makes high coding speeds possible. Also UV-curable inks can be used. If small codings do not vary much, Hot Solid Inks offer an economical alternative. Finally, glass can also be marked with especially developed glass Markers.